Data
/ˈdeɪtə/
INTRODUCTION
Data means different things to different data users, scholars and experts. One thing consistent to all stakeholder is the final output derived form data- INFORMATION.
Data is limitless and an integral part of every activity we engage in everyday. From e-mails to social media and e-commerce platforms one can only conclude that data is simply the future of ground breaking innovations.
Now let us give data a definition:
Data is simply;

1. Facts and Statistics collected together for reference or analysis
2. An assumption or a premise where inferences are done
3. Data is a set of values of qualitative or quantitative variables. Source: Wikipedia
4. Information in raw or unorganized form (such as alphabets, numbers, or symbols) that refer to, or represent, conditions, ideas, or objects
5. Data are values of qualitative or quantitative variables belonging to a set of items. Variables represent measurements of characteristics of an item.
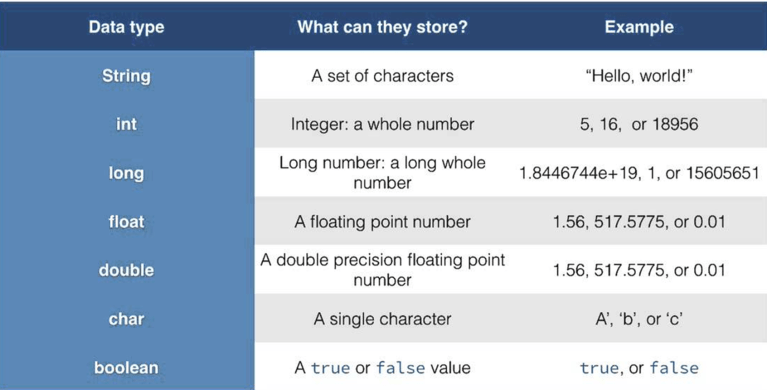
DATA TYPES
What they can store with Examples.
A great data analyst MUST understand the various data types. Throughout your data journey, you will have to work with the various data types available to help unearth insights.
TYPES OF DATA
- Qualitative Variables: Qualitative variables are not necessarily ordered, and are not necessarily measurements. Examples includes country of origin, gender, category, age group.
- Quantitative Variables: Quantitative variables are usually measured. Examples includes Height, weight, blood pressure.
Data Types that can be Analyzed
 Picture Source: BIGDATA
Picture Source: BIGDATA
- Structured Data: They are often found in databases, spreadsheets and data collection software. They include sales record, financial reports, payroll details, inventory records. They are called structured data because they are organized and in a pre-defined manner.
- Unstructured Data: They not organized in a pre-defined manner or model. They include email and instant messages, social media activities, news feeds, corporate document repositories, payment text descriptions.
Review Questions
1. What does data mean to you?
2. Can quantitative and qualitative data be structured? What is your opinion and Why?
Thank you for your response. ✨
Great! Now Let’s move to the next topic WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DATA AND INFORMATION

