Data Processing is the collection and manipulation of items of data to produce meaningful information.
To make sense of data, you should follow through all the stages of data processing.
A simple data process involves the following six(6) stages;
 Click image to Enlarge/Download
Click image to Enlarge/Download
Stage 1: Data Collection
- Data collection is the systematic approach to gathering and measuring information from a variety of sources to get a complete and accurate picture of an area of interest.
- Data collection enables a person or organization to
- Answer relevant questions,
- Evaluate outcomes and
- Make predictions about future probabilities and trends.
- Step 1: Identify issues and/or opportunities for collecting data
- Step 2: Select issue(s) and/or opportunity(es) and set goals
- Step 3: Plan an approach and/or method for data collection
- Who will the data be collected about?
- Who will the group of interest be compared to?
- What locations or geographical areas will the data be gathered from?
- What categories will be used to identify the group of interest and comparative group?
How should data be collected?
- Qualitative Data
- Quantitative Data
What sources of data should be used to collect information?
- Pre-existing or official data
- Survey data
- Interviews and focus groups
- Observed data
How long will the data be collected (the scope of data collection)?
- Step 4: Collect data
- Step 5: Analyze and interpret data
- Step 6: Act on result
Stage 2: Data Preparation
 Source: TRIFACTA
Source: TRIFACTA
- Data preparation is a pre-processing step in which data from one or more sources is cleaned and transformed to improve its quality prior to its use in business analytics.
- SAS defines data preparation as the task of blending, shaping and cleansing data to get it ready for analytics or other business purposes.
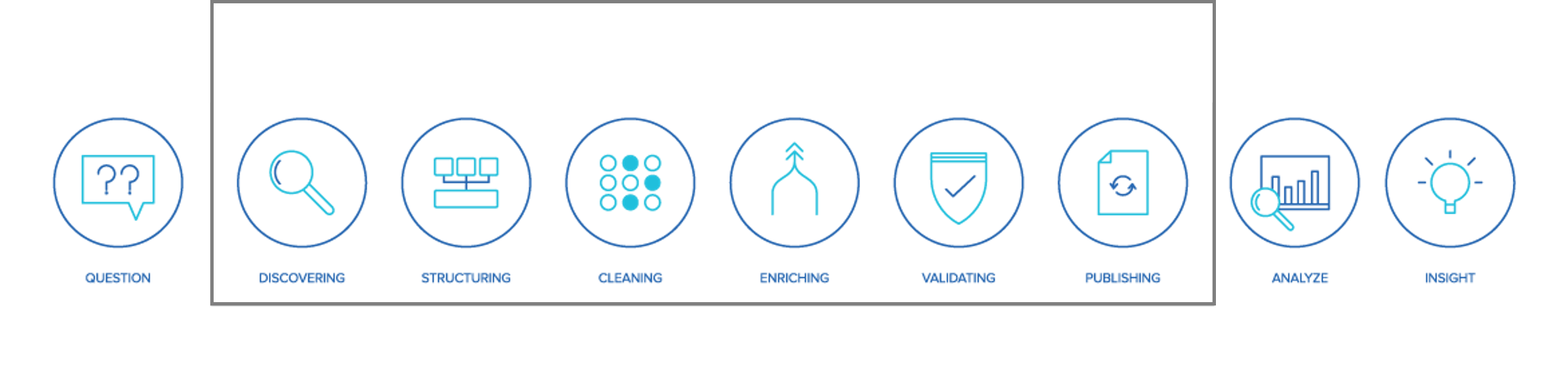
Data preparation process
This comprises of six core steps that helps the business user or data analyst turn any raw datasets into a refined information asset for accurate analysis and valuable insight. The data preparation process leads the user through a method of discovering, structuring, cleaning, enriching, validating and publishing data to be used to:
- Accelerate the analysis process with a more efficient, intuitive and visual approach to preparing data for visualization.
- Expedite data manipulation and cleansing activities so the user can focus on the real job of analysis.
- Expand the variety and complexity of data used in analysis to gain better and more valuable insight.
Stage 3: Data Entry

Data entry is the process of transcribing information into an electronic medium such as a computer or other electronic device. It can either be performed manually or automatically by using a machine or computer.
Stage 4: Data Processing

Data processing is the conversion of data into usable and desired form. This conversion or “processing” is carried out using a predefined sequence of operations either manually or automatically.
Methods of data processing
- Manual data processing: In this method, data is processed manually without the use of a machine, tool or electronic device. Data is processed manually, and all the calculations and logical operations are performed manually on the data.
- Mechanical data processing – Data processing is done by use of a mechanical device or very simple electronic devices like calculator and typewriters. When the need for processing is simple, this method can be adopted.
- Electronic data processing – This is the modern technique to process data. The fastest and best available method with the highest reliability and accuracy. The technology used is latest as this method used computers and employed in most of the agencies. The use of software forms the part of this type of data processing. The data is processed through a computer; Data and set of instructions are given to the computer as input, and the computer automatically processes the data according to the given set of instructions. The computer is also known as electronic data processing machine. Source:Planning Tank
Stage 5: Data Interpretation
Data interpretation is simply the ability to interpret, or in other words, to visualize data and make sense of the information
Stage 6: Data Storage

Data storage is the recording (storing) of information (data) in a storage medium.
One common distinction between forms of physical data storage is between random access memory (RAM) and associated formats, and secondary data storage on external drives.
Random access memory(RAM) is stored in integrated circuits for immediate use, while the data stored on hard drives, disks, flash drives and new solid state data storage units is archived for event-based access or research activities initiated by an end user.
New technologies and tech theory promote the continual expansion of data storage capability.
New solid state drives can hold enormous amounts of data in a very small device, enabling various kinds of new applications for many industries, as well as consumer uses.
Cloud services and other new forms of remote storage also add to the capacity of devices and their ability to access more data without building additional data storage into a device.
Questions:
- What is data processing?
- Explain two data processes stages?
- Outline the six(6) core steps of Data Preparation?
CONGRATULATIONS!
You have completed the Beginners Class! It’s time to do a review of what you have learnt and earn a verified certificate of completion. CLICK to BEGIN.



