At the end of this Topic;
- We should have a deep understanding of what a Variable is?
- The Different Variable Types.
- Why Variables are important in Data Analysis.
What is a Variable?
Variable comes from the word ‘Vary’ which simply means change . This change could be from one condition, form, or state to another.
A variable is simply defined as an Element, a Feature or a factor that is liable to change. An example of an element in a mathematical equation is x+1=3. Where x is referred as the variable liable to change.
A variable could also be a symbol or a number we do NOT know yet. From the example above in x+1=3, it is clear that the symbol x is a symbol we do not know yet.
Another definition of a variable is a value that can change depending on conditions or an information passed to a program. In the case of our example x+1=?, If a condition is passed as where x=2. The equation becomes 2+1=3. When 2 is replaced as a condition for x.
Just like in Data Types we also have Two(2) variable types as every variable represents a form of data.
Why are Variables important in Data Analysis?
Variables are important in data analysis as they are key to understanding relationships in data to draw the right conclusion from a statistical analysis.
Types of Variables
We have two types of variables;
- Quantitative Variables
- Qualitative Variables
Review Questions
Give a summary of Variables in your own words with examples


Very Enlightening.
Variables:
*Elements, symbols, factors, or features whose values may either be unknown, vary or change based on set conditions.
Quantitative (Discreet and Continuous) variables, and Qualitative (Nominal, Ordinal and Binary) variables.
Had it been we have only two types of gender(Male or Female), it would be classified as Binary; but now, we have other genders aside M & F.
Thanks for the information.
LikeLike
Short, precise, yet educative.
Based on further research, I was able to realize the following types of Variables:
1. Independent Variable
2. Dependent Variable
3. Controlled Variable
4. Extraneous Variable
In all, they can be categorized as either; QUALITATIVE or QUANTITATIVE VARIABLES.
Thanks.
LikeLiked by 1 person
This reminds me of undergraduate days studying Statistics.
Qualitative (Normal, Ordinal, binary) and Quantitative (discrete and continuous) variable.
Thanks for this.
LikeLike
Summary
Variables are symbols are numbers or symbols that we do not know yet.
They are liable to change and dependent on factors and circumstances.
As an Economist,I remember factors of production and how we have fixed and variable factors.
LikeLike
As it was defined concisely.. Variable are those factors, element that are not stable, they are dynamic and liable to change based on the conditions set to it.
Types of variables…
Quantitative ( discrete and continuous)
Qualitative (norminal, binary and ordinary)
LikeLike
Variables are characters, features that are unknown and are likely to change depending on the conditions or information influencing them.
The two broad categories of variables are quantitative and qualitative variables.
While quantitative are actual measurable values with subcategory of discrete variables and continuous variables, qualitative variables are descriptive variables in subcategories of nominal variables, ordinal variables and binary variables.
Example of quantitative variable is height, number of locations to examine in a data sheet.
Example of qualitative variables is performance levels of students in a course.
Thanks for the refresher course! Insightful.
LikeLike
Variables can be described as containers used in holding data meant to be manipulated during a data processing session.
A variable is simply defined as an Element, a Feature or a factor that is liable to change.
The 2 types of variables are:
1. Quantitative Variables
2. Qualitative Variables
LikeLike
Variable means having tendency to change or deviate from a current state to another as other factor changes.
For example in costing, variable cost refers to cost that vary with output. Direct labour and direct material are variable cost associated with production.
LikeLike
Variables have no fixed value, and can depend on other factors. Quantitative variables can be quantified or numbered (in terms of quantity) eg number of chairs, tables etc. While qualitative variables cannot be quantitfied or numbered ( eg colour, working condition etc) While quantitative variables could be discrete or continuous data types qualitative variables are ordered, nominal or binary.
LikeLike
Variables is anything (elements, features or factors ) that is not static but liable to change as a result of many factors such as conditions, form, state, etc.
It could also be a symbol or a number we do NOT know yet. E.g. y+1=3. The symbol ‘y’ is not know yet.
As a value that can change depending on conditions or information passed to a program, it implies that variable changes when some conditions are fulfil. E.G. y+1=?, If a condition is passed as where y=2. The equation becomes 2+1=3. When 2 is replaced as a condition for y.
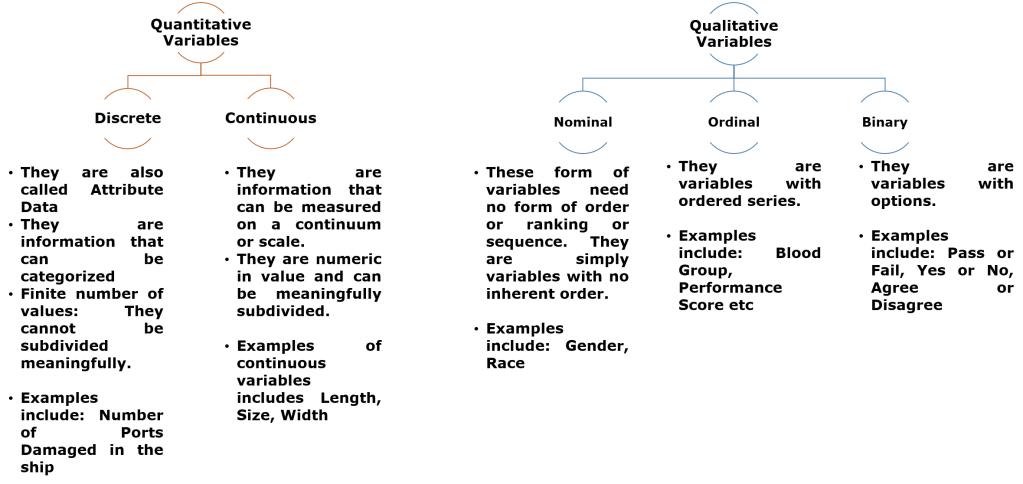
Every variable represents a form of data, and there are of two (2) types. They are Quantitative and Qualitative.
The Quantitative variables are further divided into Discrete and Continuous.
While the Discrete variables also called attributes data, are information that can be categorized, an finite numbers of values and cannot be subdivided meaningfully. E.g. number of SLA bridges. The Continuous variables on the other hand are information that can be measured on a continuum or scale. They are numeric in value and can be meaningfully subdivided. E.g. length, size etc.
The Qualitative variables are variable that can be quantified and are subdivided into Nominal, Ordinal and Binary.
The Nominal variables are form of variables that need no form of order or ranking or sequence; but are simply variables with no inherent order. E.g. Gender, race etc.
The Ordinal variables are variables with ordered series, either in ascending or descending, top 5 or top 10 marks. E.g. blood group, performance scores
The Binary variables are variables with options, such as having two (2) options to select. E.g. Yes or No, Agree or Disagree, Pass or Fail etc.
LikeLike